International
| NexMPI – Zobrazovanie magnetických častíc pre teranostiku novej generácie a medicínsky výskum | |
| Magnetic Particle Imaging for next-generation theranostics and medical research | |
| Program: | COST |
| Project leader: | RNDr. Kubovčíková Martina , PhD. |
| Duration: | 22.10.2024 – 21.10.2028 |
| SeNaTa – Magnetické nanoštruktúrne materiály schopné samozahrievania pre teranostické aplikácie | |
| Self-heating magnetic nanoconstructs for theranostic applications | |
| Program: | Bilateral – other |
| Project leader: | RNDr. Kubovčíková Martina , PhD. |
| Annotation: | Cancer is still one of the leading causes of death worldwide, therefore significant research and innovation efforts are still needed to find new materials and methods for better cancer diagnosis and treatment. Magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) appear to be a very promising material for use in many medical fields, such as in nanosurgery they can be used to kill tumor cells by increasing drug concentration in target cells in combination with hyperthermia as well. The presented project is focused on the development of new nanoconstructs labeled by radionuclide as a potential theranostic agent for radiotherapy and diagnostics. The first step to achieve the desired goal will be the synthesis of nanoconstructs consisting of self-heating magnetic nanoparticles coated with various biocompatible substances, which will exhibit the desired bioactivity as well. The prepared nanoconstructs will be studied by several physicochemical methods, and their stability and suitability for magnetic hyperthermia, i.e. the ability to produce heat in an alternating magnetic field, will be monitored. In the second step, nanoconstructs with the best properties will be radiolabeled with therapeutic 177Lu and diagnostic 99mTh radionuclides to prepare radioactive nanoconstructs for dual therapy and diagnosis. In the next step, in vitro toxicity testing of nanoconstructs labeled with radionuclides will be performed. The prepared magnetic magnetic nanostructured materials labeled with radionuclides will contribute to the improvement of diagnostics and therapy of cancer diseases. The project is based on a complex multidisciplinary approach, from physics, chemistry to biochemistry and biomedicine. The involved partners possess key skills, infrastructure and are highly motivated to achieve the project goals. |
| Duration: | 1.7.2023 – 30.6.2025 |
| MultiFunMag – Návrh a príprava multifunkčných magnetických nanočastíc na detekciu nádorových buniek | |
| Design and preparation of multifunctional magnetic nanoparticles for the cancer cell detection | |
| Program: | Multilateral – other |
| Project leader: | Ing. Závišová Vlasta, PhD. |
| Annotation: | Cancer is the second leading cause of death after cardiovascular disease in almost all European countries. Over the past several decades, the principle types of cancer therapies have been chemotherapy, radiation therapy and surgery. This project is focused on the development of biocompatible multifunctional magnetic nanoparticles and evaluation of their diagnostic andtherapeutic potential for the application in oncology. The first step to achieve the desired goals will be the synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles and the functionalization of their surface with a suitable biocompatible materials suitable for radiotracer binding. Several physicochemical methods will be used to optimize the preparation of biocompatible multifunctional magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs). At the same time, we will study the suitability of multifunctional magnetic nanoparticles for magnetic resonance imaging and magnetic hyperthermia application as well. Considering the application purposes of biocompatible multifunctional magnetic nanoparticles, biodistribution studies of radiotracer conjugated MNPs will be conducted. The prepared radiotracer conjugated MNPs will improve the efficacy of cancer diagnosis and treatment. Moreover, combination of MRI, hyperthermia and radiotherapy represents a significant advance in cancer diseases treatment and a substantial improvement in survival of oncological patients. The project is based on a complex multidisciplinary approach,ranging from physics, chemistry up to biochemistry and biomedicine. The involved partners possess key skills, infrastructure and are highly motivated to reach the project goals. |
| Duration: | 1.3.2020 – 31.12.2022 |
| Nanoradiomag – Vývoj a príprava rádionuklidmi značených magnetických nanočastíc dispergovaných vo vodnom prostredí. | |
| Development and production of water-dispersible radionuclide labeled magnetic nanoparticles | |
| Program: | EUREKA |
| Project leader: | Ing. Koneracká Martina, CSc. |
| Duration: | 1.1.2018 – 31.12.2020 |
| NANOUPTAKE – Prekonanie bariiér pre komerčné využitie nanokvapalín (NANOUPTAKE) | |
| Overcoming Barriers to Nanofluids Market Uptake ( NANOUPTAKE) | |
| Program: | COST |
| Project leader: | RNDr. Timko Milan, CSc. |
| Annotation: | Nanofluids are defined as fluids that contain nanometre-sized particles with enhanced heat transfer properties. Nanofluids improve the efficiency of heat exchange and thermal energy storage. In addition, nanofluids fall within one of the Key Enabling Technologies (KET) supported by the European Commission. Although some nanofluid commercial applications currently exist, most of the current nanofluids are at Technological Readiness Levels (TRL) 1 to 3. Most of the nanofluids research in COST countries has been conducted by Research, Development and Innovation (R+D+i) centres through national funding. Additional coordinated research and development efforts are required to develop nanofluids up to higher TRL levels and to overcome commercial application barriers. If these barriers are overcome, nanofluids will be an important player in the Value Added Materials (VAM) for the energy sector.The objective of the NANOUPTAKE COST Action is to create a Europe-wide network of leading R+D+i institutions, and of key industries, to develop and foster the use of nanofluids as advanced heat transfer/thermal storage materials to increase the efficiency of heat exchange and storage systems. |
| Project webpage: | http://www.cost.eu/COST_Actions/ca/CA15119 |
| Duration: | 19.4.2016 – 18.4.2020 |
| RADIOMAG – Multifunkcionalizované nanočastice pre magnetickú hypertermiu a nepriamu radiačnú | |
| Multifunctional Nanoparticles for Magnetic Hyperthermia and Indirect Radiation Therapy | |
| Program: | COST |
| Project leader: | doc. RNDr. Kopčanský Peter, CSc. |
| Annotation: | The Action aims to bring together and to organise the research outcomes from the different participating network members in a practical way to provide clinicians with the necessary input to trial a novel anti-cancer treatment combining magnetic hyperthermia and radiotherapy, also identifying future research objectives upon appraisal of the obtained results. Feedback between the different working groups here is essential, and is expected that the lifetime of this Action proposal will eventually result in a compendium of best practices for magnetic hyperthermia.RADIOMAG will generate new and strengthen the existing synergies between technical advances (thermal imaging / MH), new treatment concepts (combined targeting radiosensitisation and magnetic thermotherapy) and biocompatible coating in order to achieve a breakthrough in the clinical application of magnetic hyperthermia. Due to the complexity of this aim, synergies can only be achieved on a longer time frame, by means of workshops, STSMs, joint publications, common Horizon 2020 research proposals and exchange with other COST Actions (e.g. TD1004, TD1205). |
| Project webpage: | http://www.cost-radiomag.eu/ |
| Duration: | 13.11.2014 – 12.11.2018 |
National
| Funkcionalizované magnetické nanočastice pre MRI zobrazovanie distribúcie liečiva v pľúcach pri experimentálnom syndróme akútnej respiračnej tiesne (ARDS) | |
| Functionalized magnetic nanoparticles for MRI imaging of drug distribution in the lungs in experimental acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) | |
| Program: | VEGA |
| Project leader: | Ing. Koneracká Martina, CSc. |
| Annotation: | The current project is focused on the synthesis and functionalization of magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) for MRIimaging of the drug N-acetylcysteine distribution in the lungs in experimental acute respiratory distress syndrome(ARDS). The first step will be to prepare a conjugate consisting of MNPs modified with functional groups suitablefor drug conjugation. MNPs functionalization and drug conjugation will be optimized and studied byphysicochemical methods such as UV/Vis and IR spectroscopy, microscopy, calorimetry or magneticmeasurements. In the next phase, the conjugate will be analyzed by MRI and compared with the properties ofcommercially available MRI contrast agents. In the third step, the relevant ARDS model will be created, and theconjugate will be applied to the lungs. Finally, the conjugate will be imaged using optimized MRI techniques tostudy the drug distribution in the lungs in ARDS. The output items of the project have a direct application potentialfor clinical practice. |
| Duration: | 1.1.2023 – 31.12.2026 |
| NANOVIR – Nanočastice pre riešenie diagnosticko-terapeutických problémov s COVID-19 (NANOVIR) | |
| – | |
| Program: | Štrukturálne fondy EÚ Výskum a inovácie |
| Project leader: | Ing. Závišová Vlasta, PhD. |
| Project webpage: | https://websrv.saske.sk/uef/veda-a-vyskum/projekty-v-ramci-opvai/nanovir/ |
| Duration: | 3.3.2021 – 30.6.2023 |
| BIOVID-19 – Vývoj biomodelov pre zlepšenie hodnotenia účinnosti liekov a látok, ktoré majú potenciál pri liečbe COVID-19 (BIOVID-19) | |
| – | |
| Program: | Štrukturálne fondy EÚ Výskum a inovácie |
| Project leader: | Ing. Koneracká Martina, CSc. |
| Project webpage: | https://websrv.saske.sk/uef/veda-a-vyskum/projekty-v-ramci-opvai/biovid-19/ |
| Duration: | 29.6.2021 – 30.6.2023 |
| Funkcionalizácia magnetických nanočastíc na detekciu rakovinových buniek | |
| Functionalization of magnetic nanoparticles for cancer cell detection | |
| Program: | VEGA |
| Project leader: | Ing. Koneracká Martina, CSc. |
| Annotation: | The presented project is focused on the preparation of a magnetic biocomplex that specifically detects cancer cells; it penetrates into their structure and enables better visualization of the affected areas, using magneticresonance imaging (MRI), for example. The surface of synthetized magnetic nanoparticles will be functionalized bydifferent amino acids. Several physicochemical methods (spectroscopic, microscopic, calorimetric, magnetic andothers) will be used to optimize the nanoparticle functionalization. We will also study the suitability of usingmodified nanoparticles for MRI. The next step will be the conjugation of a specific antibody to the functionalizednanoparticles (biocomplex) and the study of cell interaction with biocomplex by immunochemical methods.Considering the application purposes of magnetic nanoparticles, one of our goals will be investigation the effect ofprepared magnetic biocomplexes on cell viability in combination with magnetic hyperthermia. |
| Duration: | 1.1.2019 – 31.12.2022 |
| Makroskopicky anizotrópne kompozity na báze kvapalnych kryštálov a magnetických nanočastíc | |
| Macroscopic anisotropic composites based on liquid crystals and magnetic nanoparticles | |
| Program: | VEGA |
| Project leader: | RNDr. Tomašovičová Natália, CSc. |
| Annotation: | The proposal targets basic research on composite materials consisting of liquid crystals and various magnetic nanoparticles. Combination of the anisotropic properties of liquid crystals with the magnetic properties of the nanoparticles results in composites with unique magnetic and optical properties that the component materials themselves do not possess. The proposed studies concentrate on the increase of the sensitivity of our composite soft matter materials (liquid state) to magnetic fields and prepare new materials having unique dielectric, magnetic and optical properties. The main goal of the proposal is to influence the sensitivity of these anisotropicsystems to external magnetic field by adding suitable magnetic nanoparticles and by this way make a step forward towards potential applications in various magneto-optical or dielectric devices as for example sensors of low magnetic fields or light shutter. |
| Duration: | 1.1.2017 – 31.12.2020 |
| MVISION – Nanočastice v anizotrópnych systémoch | |
| Nanoparticles in anisotropic systems | |
| Program: | SRDA |
| Project leader: | doc. RNDr. Kopčanský Peter, CSc. |
| Annotation: | The proposal is devoted to study complex anisotropic systems based on thermotropic as well as lyotropic(biological) liquid crystals. Liquid crystals represents the uniq state of matter, which is liquid but posses theanisotropic properties. The structuralization phenomena in such systems play key role in fundamental as well asin applied research. The main aim is to s influence the sensitivity of these anisotropic systems to externalmagnetic field, what will be done by adding suitable magnetic nanoparticles and open the way for theirapplications in magneto-optical devices. |
| Duration: | 1.7.2016 – 31.12.2020 |
| Interakcia magnetických kvapalín s elektromagnetickým poľom | |
| Interaction of magnetic fluids with electromagnetic field | |
| Program: | VEGA |
| Project leader: | RNDr. Timko Milan, CSc. |
| Annotation: | The proposed project will be devoted to the study magnetic principle of heating mechanism – hyperthermia in magnetic nanoparticles systems in dependence on preparation process, size and size distribution and magnetic properties. Besides usually used biocompatible spherical anoparticles as a subjects of this proposal will be special prepared magnetosome and magnetoferritin containing spherical magnetite nanoparticles. The obtainedexperiences for achievement high specific heat power will enable the application magnetic nanoparticles at cancer treatment in biomedicine.We aim to investigate the shielding (absorption and reflection) effects of transformer oil based magnetic fluid.Besides the unique cooling and isolating properties, these magnetic fluids can be reliable shielding medium in electromagnetic devices as well. The research on radiation stability of MFs will address electromagnetic fields and another type radiation. |
| Duration: | 1.1.2016 – 31.12.2019 |
| GONanoplatform – Grafénová nanoplatforma na detekciu rakoviny | |
| Graphene-based nanoplatform for detection of cancer | |
| Program: | SRDA |
| Project leader: | Ing. Koneracká Martina, CSc. |
| Annotation: | This project proposal reflects current technological progress and new opportunities in biomedical applications ofgraphene-based sensors. Our main goals include the design and development of a graphene oxidemultifunctional nanoplatform (GO-MFN) for the detection of tumor cells. In the first step, the development ofgraphene oxide nanoflakes of appropriate size functionalized by monoclonal antibody is planned. For sensingthe tumor cells, GO-MFN of 100 nm size able to interact with a single cell will be prepared. Magneticnanoparticles added to GO-MFN will enable the inspection of deep tissues by nuclear magnetic resonance. Thedegree of oxidation of GO, type of the functional groups, optimal functionalization with covalently boundmonoclonal antibodies and magnetic nanoparticles, are the most important technological steps. The analysis ofthe basic interactions related to tumor sensing will be conducted in vitro on 2D and 3D cell models up to theproof-of-principle stage that will be directly applicable to laboratory and preclinical testing. The GO-MFNinteraction with the cell membrane and with the cell interior will be analysed with subcellular resolution. Such anapproach will bring original knowledge and a detailed understanding of the tumor sensing process that isimportant for the optimization of the sensor sensitivity. Detection of biomolecules bound to GO-MFN will be addressed in real time by several techniques.The project is based on a complex multidisciplinary approach, ranging from physics and chemistry up tobiomedicine and combining excellent science and the most sophisticated nano and bio-engineering. Theinvolved partners possess key skills, infrastructure, antibodies and tumor models, and are highly motivated toreach the project goals. |
| Duration: | 1.7.2015 – 30.6.2019 |
| NANOSIMKA – Účinok nanoenkapsulovaného simvastatínu na kardiovaskulárny systém pri experimentálnom metabolickom syndróme | |
| Effects of nanoencapsulated simvastatin on cardiovascular system in experimental metabolic syndrome | |
| Program: | SRDA |
| Project leader: | Ing. Závišová Vlasta, PhD. |
| Annotation: | High level of cholesterol in the blood increases the risk of heart and vascular diseases. Simvastatin reduces cholesterol production in the liver thus reduces the blood cholesterol level. Long-term use of statins has been associated with the occurrence of side effects, which in addition increase with increasing their dose. In particular, the statin side effect include mainly inhibition of the endogenous synthesis of CoQ10 – basic cofactor for ATP synthesis and paradoxically activation of PCSK9 – an important enzyme for the synthesis of LDLcholesterol.The project aims to increase the bioavailability of simvastatin in the liver, thus reducing the daily dose and consequently to prevent the reduction of CoQ10 levels as well as to block the activation of PCSK9. In order to achieve this this aim, nano-encapsulated simvastatin together with nano-encapsulated CoQ10 or PCSK9 inhibitor, or in the polymer with antioxidant properties will be prepared, tested and applied. This ensuresthe targeted transport of simvastatin to the liver simultaneously with CoQ10, or inhibitor of PCSK9, or simultaneous increase in antioxidant capacity. In the case of successful results the proposed project may uncover new possibility of using nanocarriers for the treatment of metabolic and cardiovascular diseases. |
| Duration: | 1.7.2015 – 30.6.2019 |
| Citlivosť kvapalných kryštálov s nanočasticami na vonkajšie magnetické pole | |
| Sensitivity of liquid crystals containing nanoparticles to external magnetic field | |
| Program: | VEGA |
| Project leader: | doc. RNDr. Kopčanský Peter, CSc. |
| Annotation: | The proposed project will devoted to the study of composite systems of liquid crystal with nanoparticles mainly magnetic particles with the aim to change their sensitivity to external magnetic field. The object of such study will be new kind of liquid crystals with bent-core molecules as well as traditional calamitic liquid crystals with rod-like molecules. Also the influence of magnetic particles on the structural phase transition from isotropic to nematic phase in external magnetic field will be investigated. We suppose this structural transition will be induced by external magnetic field. Moreover, the response of the above mentioned composite systems to low magnetic field (up to 0.1T) will be investigated, which is important for the construction of various magneto-optical devices as for example maping of magnetic fields. |
| Duration: | 1.1.2013 – 31.12.2016 |
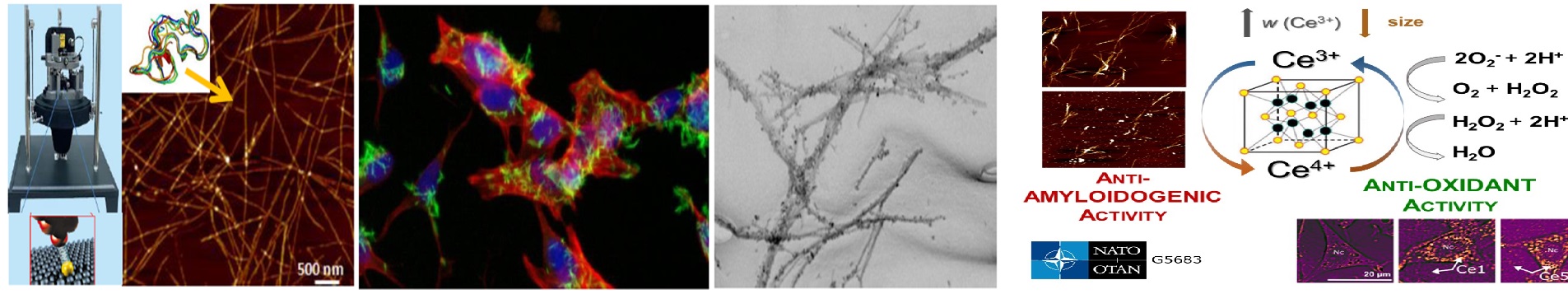
| Štrukturalizačné javy v samousporiadajúcich štruktúrach proteínov ovplyvňované nanočasticami | |
| Structure-forming phenomena in self-assembly structures of proteins influenced by nanoparticles | |
| Program: | VEGA |
| Project leader: | Ing. Koneracká Martina, CSc. |
| Annotation: | The main goal of the project is to study and explain the interaction of nanoparticles with proteins. Particularlysearch of correlation among size, shape, surface charge and magnetic moment of the nanoparticles and theirability to influence the structuralization effects on proteins there will be found out. The study of structural changesand amyloid aggregation of proteins is very intensive in the last decade, from times of the discovery that a varietyof human disorders is associated with the presence of amyloid deposits in various tissues and organs. Theamyloid related diseases, including Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases, appear as a result of fail of protein’sfunction caused their incorrect folding or aggregation of protein molecules in to specific, highly organized selfassembly structures of proteins (protein amyloid aggregates). |
| Duration: | 1.1.2012 – 31.12.2015 |
| NANOALIS – Účinok aliskirénu viazaného na nanočastice pri experimentálnej hypertenzii | |
| The effect of aliskiren loaded nanoparticles in experimental hypertension | |
| Program: | SRDA |
| Project leader: | Ing. Koneracká Martina, CSc. |
| Annotation: | Renin, the protease enzyme, activates the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) by cleaving angiotensinogen to yield angiotensin I, which is further converted into angiotensin II.Therefore, blockade of renin production may represent an effective inhibition of whole RAAS. Aliskiren is the first in a class of drugs called direct renin inhibitor with high specificity. The limiting factor in clinical praxis might be, however, the relatively low bioavailability of aliskiren. The aim of this project is to decrease degradation and to increase bioavailabilityof the renin inhibitor-aliskiren and to maximalize the effect of aliskiren on kidney function and structure.Decrease of blood pressure will be thus effectively achieved by inhibition of the first step in RAAS activation. To increase bioavailability of aliskiren nanoencapsulation of this drug (nanoalis)and magnetic nanoencapsulation will be performed followed by application and biological analysis of encapsulated aliskiren forms.While encapsulation assuse decrease of degradation and increase of bioavailability, magnetization amplifies direct delivery of aliskiren to the target tissue of renin production-the kidney.By this way renoprotective effect of aliskiren besides blood pressure reduction will be achieved.In case of seccessful results,qualitatively new way in the treatment of hypertension and new drug delivery may be supposed. |
| Duration: | 1.5.2011 – 31.10.2014 |
 Contact
Contact Intranet
Intranet SK
SK